
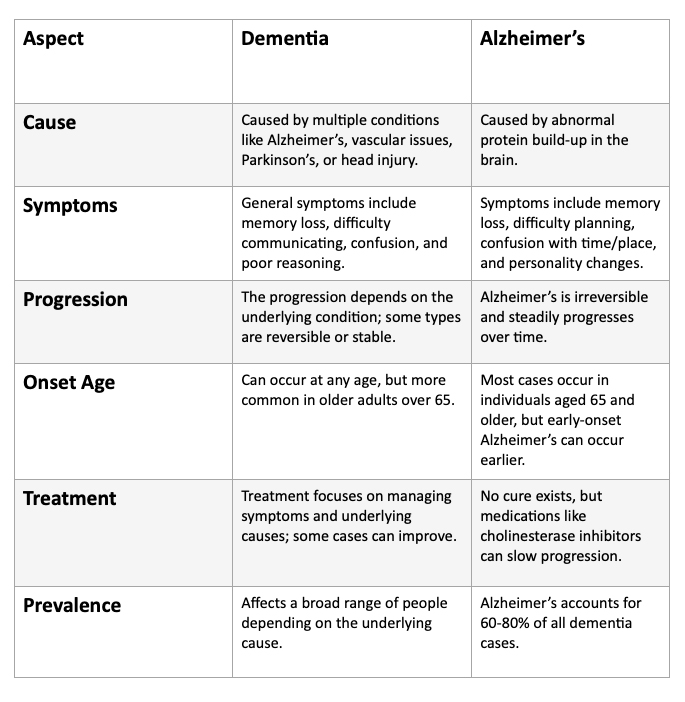
People often get confused amongst the two medical terms - dementia and Alzheimer's and take them as synonyms. Rather, dementia is a generic term that includes all types of memory loss and thinking issues, whereas Alzheimer's is one of the diseases that affects the brain and is the cause for dementia.
According to a report by the Alzheimer’s Association, around 6.9 million Americans who are aged 65 and above have Alzheimer’s in 2024, thus showcasing how fast the number of patients are growing. But what are the differences between the two of them? Which one is worse? Let’s discuss it over here.
What are Dementia and Alzheimer's?
Before diving into which is worse: dementia or Alzheimer's, and studying their differences, it's best to get a clear understanding of the two.
Dementia
It is a term that is used when an individual is suffering from a decline in cognitive abilities. The symptoms of dementia usually include behavior and memory changes, but there are plenty more indications.
There are different types of dementia, each with specific symptoms. For example, vascular dementia occurs when there is slowness of thought. Individuals who suffer from difficulty in movement may have Lewy body dementia.
Alzheimer's
Globally, Alzheimer's is said to be the most common cause of dementia. It is a degenerative condition that keeps getting worse as time passes by. The earliest symptom of Alzheimer's that people suffer from is short-term memory loss. After some time, the symptoms widen from having movement issues to losing the ability to speak.
Differences between Alzheimer's and Dementia
Other Types of Dementia
Apart from Alzheimer's, there are plenty more types of diseases that might share the same symptoms. This makes it difficult to identify the correct type. Here are a few other forms that individuals suffer from:
Mixed Dementia:
As the name suggests, this condition includes more than one type of symptom. The most common form of this type of dementia is vascular dementia and Alzheimer's.
Frontotemporal Dementia:
It is a progressive form of dementia that usually occurs around the age of 45-60 years. It affects the nerve cells in the front and side areas of the brain. It is one of the rare types of dementia, and currently, there is no cure for it.
Vascular Dementia:
It is usually caused due to brain damage that results in disruption of blood flow to the brain due to brain hemorrhage or stroke. The symptoms might start mild but gradually worsen, especially when a person suffers from a stroke.
Lewy Body Dementia:
Caused by an abnormal buildup of proteins around the brain, this progressive disease is estimated to be the third most common type of dementia among Americans.
Can Dementia or Alzheimer's be Prevented?
There is no guarantee whether dementia or Alzheimer's can be prevented, although adopting a healthy lifestyle can reduce the risk of getting this disease significantly. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and regular physical activity like brisk walking or swimming can contribute to brain health.
Keeping the mind active through puzzles, reading, or learning new skills, as well as maintaining strong social connections, is also crucial. Additionally, managing health conditions such as high blood pressure, diabetes, and high cholesterol can further lower the risk. While these strategies may help reduce the risk, early diagnosis and treatment remain essential for slowing the progression of the disease.
Conclusion
Alzheimer's is a type of dementia and often has overlapping symptoms with the other types. If you are concerned for the well-being of your loved one and feel that they might have symptoms similar to those stated above, then it’s better to talk with a healthcare professional as soon as possible. This will not only help you determine the severity of the issue but will also provide you with clear information on the type that you are suffering from.
